You can track your single origin coffee beans using modern digital tools that combine QR codes and blockchain technology.
Start by scanning the QR code on your coffee package to access detailed origin information, real-time tracking data, and processing methods.
Microsoft Azure Blockchain platforms connect you directly with farmers and verify sustainability certifications.
Understanding your bean’s pathway through digital traceability reveals a complex network of geographical elements, processing techniques, and ethical sourcing practices.
Key Takeaways
- Scan QR codes on packaging to access digital tracking systems that reveal detailed origin information and real-time supply chain updates.
- Verify authenticity through certification labels like C.A.F.E. Practices and Fairtrade that confirm ethical sourcing and sustainability practices.
- Check processing methods (washed, natural, honey, or wet-hulled) which indicate regional characteristics and help trace geographical origins.
- Use mobile apps connected to blockchain tracking systems to view farm-specific data and establish direct connections with producers.
- Examine flavor profiles against regional characteristics to validate origin claims, as terroir creates distinct taste signatures.
Understanding Digital Traceability Tools
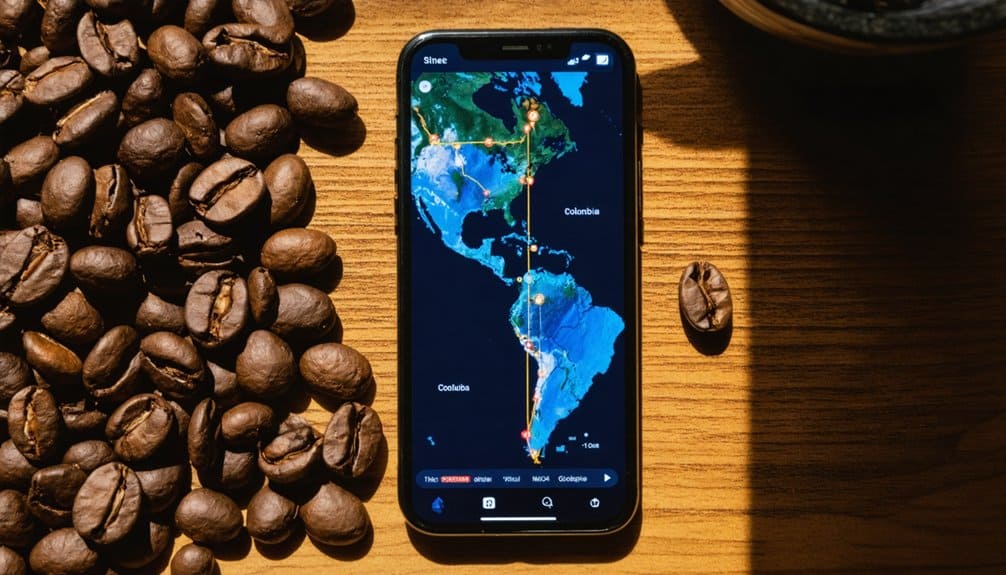

When tracking a coffee bean’s path from farm to cup, digital traceability tools have revolutionized supply chain transparency.
You’ll find these systems utilize QR codes and blockchain technology to create an unbroken chain of documentation, allowing you to verify your coffee’s authenticity and origin.
First developed with Microsoft Azure Blockchain, the tool enables seamless tracking across the global supply chain.
As a conscious coffee consumer, you’re now able to access detailed information about your beans through mobile apps that display real-time updates.
These platforms connect you directly with producers, showing farming practices and handling processes.
Through blockchain-secured data sharing, you’re joining a community that values accountability and authenticity in every cup.
Decoding Your Coffee’s Origin Story
As you investigate your coffee’s origin story, understanding its historical roots becomes essential for appreciating the complex path from uncovering to your cup.
You’ll find that coffee’s odyssey began in Ethiopia, where a herder named Kaldi initially observed its energizing effects on goats.
From there, your bean’s ancestral path likely traces through Yemen, where Sufi monasteries welcomed it for spiritual practices.
Today, you can pinpoint your coffee’s exact origins through single-origin designations.
Whether you’re sipping Ethiopian Yirgacheffe’s floral notes or savoring Brazilian Santos’ nutty profile, each cup connects you to a specific farm, season, and processing method, revealing the unique terroir of its source.
Coffee’s remarkable spread to the Arabian Peninsula helped establish first coffee houses in Constantinople, forever changing how people socialized over their daily brew.
The Role of Geographical Elements
Geography stands as the fundamental architect of your coffee’s character, orchestrating a complex interplay of environmental factors within the “Bean Belt.”
This equatorial zone, stretching between the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn, houses diverse growing regions where altitude, soil composition, and weather patterns converge to create distinct flavor profiles.
Your coffee’s unique attributes emerge from:
- Altitude ranges of 800-2,200 meters, where thin air and cooler temperatures slow berry development
- Mineral-rich volcanic soils that infuse beans with region-specific characteristics
- Consistent weather patterns that regulate growth cycles
- Precise latitudinal positioning that guarantees ideal sunlight and temperature exposure
Southeast Asia’s distinct coffee heritage dates back to the late seventeenth century, when cultivation first began in this vibrant region.
Processing Methods and Their Impact
The transformation of coffee cherries into exportable green beans relies on distinct processing methods that fundamentally shape your coffee’s final flavor profile.
You’ll encounter four primary methods: washed, natural, honey, and wet-hulled processing.
Each method creates unique characteristics – washed processing yields bright, crisp notes through careful fermentation, while natural processing develops sweeter, fruit-forward flavors during sun-drying.
Honey processing offers a balanced middle ground, allowing varying degrees of mucilage retention.
In regions like Indonesia, wet-hulled processing adapts to humid climates, resulting in distinctive earthy profiles that connect you to specific origin stories.
Achieving the proper moisture content during drying is essential for preventing fungal growth and maintaining bean quality.
Exploring Regional Flavor Profiles

Your single origin coffee’s flavor profile directly correlates to its geographic origin, where factors like soil composition, altitude, and climate create distinct taste characteristics known as terroir.
You’ll find that African coffees typically showcase bright, fruity notes while Central American beans lean toward chocolate and nutty profiles, and Asian coffees often present earthy, full-bodied characteristics.
Beyond terroir, processing methods greatly shape these regional profiles, with wet-processed African coffees highlighting their natural acidity and dry-processed Asian beans emphasizing their bold, intense flavors.
These distinct characteristics are found primarily in coffees grown along the Bean Belt, the equatorial region between 25 degrees north and south of the equator.
Geographic Taste Characteristics
Each coffee-growing region imparts distinct flavor characteristics that stem from its unique combination of climate, soil composition, altitude, and cultivation methods.
When you’re exploring single-origin beans, you’ll encounter these key geographic patterns:
- African beans deliver bright acidity with floral-fruity profiles, featuring notes of berries and citrus. These beans thrive in sweet soil conditions at higher elevations.
- Central American coffees balance medium-high acidity with nutty undertones, improved by volcanic soils
- South American beans offer low-moderate acidity with chocolate-caramel notes and creamy textures
- Indonesian varieties present heavy-bodied, earthy profiles with distinctive spice characteristics
Understanding these regional markers helps you identify your bean’s origin and anticipate its flavor profile.
Terroir’s Impact on Coffee
Across major coffee-growing regions worldwide, terroir shapes distinctive flavor profiles through complex interactions between climate, soil composition, and topography.
You’ll uncover African beans express bright acidity with bergamot and jasmine notes, particularly in Ethiopian varieties, while Kenyan coffees showcase bold blackberry undertones.
Central and South American regions yield balanced profiles featuring cocoa and caramel notes, especially evident in Colombian and Costa Rican beans.
Indonesia’s tropical environment produces full-bodied cups with earthy, spice-forward characteristics, while Pacific Island coffees offer unique depth with sweet, tropical complexity.
Vietnamese highlands cultivate beans with higher caffeine content due to their Robusta-focused production.
Understanding these regional signatures helps you pinpoint your bean’s origin story.
Processing Methods Matter
While terroir sets the foundation for coffee’s character, processing methods amplify and transform these inherent qualities into distinct flavor profiles.
You’ll find that each method creates unique characteristics, from natural processing’s sweet, fruit-forward notes to washed processing’s bright, clean flavors.
Sumatran coffees exemplify how wet-hulling processing methods create their signature rich, full-bodied character.
Key processing methods shape your coffee’s final taste:
- Natural processing improves body and sweetness through 2-4 weeks of controlled drying
- Washed processing delivers cleaner, more acidic notes
- Honey processing balances sweetness with moderate acidity
- Wet-hulled processing creates distinctive earthy, spicy profiles
Understanding these methods helps you trace your bean’s path from origin to cup.
Verifying Bean Authenticity
In the current evolving coffee market, verifying the authenticity of single-origin beans has become increasingly critical through advanced analytical methods.
You’ll find that High Performance Anion Exchange Chromatography (HPAEC) stands at the forefront of verification, analyzing both free and total sugar content in your beans according to ISO 11292:1995 standards.
Water extraction remains the only permissible method for processing authentic coffee products.
When you’re sourcing premium beans, GC-MS-based multimarker profiling and metabolic fingerprinting help authenticate your coffee’s origin.
These techniques identify unique chemical patterns and critical markers through principal component analysis.
Regular authenticity checks protect you from fraudulent products while ensuring compliance with regulations like Directive 1999/4/EC, maintaining both market integrity and your trust.
From Farm to Cup: Following the Trail

You’ll find modern coffee tracing systems employ digital platforms that monitor your beans from harvest through processing, shipping, and roasting.
Your single-origin coffee‘s path spans multiple stages: natural or washed processing that takes weeks, a 2-4 month shipping period in jute bags, and ultimately a precise 10-15 minute roasting transformation.
Through these tracking tools, you can verify your beans’ progression through each critical phase, from their origin in specific Coffee Belt regions to their final roasted form.
Coffee trees require about five years of growth before producing enough cherries for one pound of roasted beans annually.
Digital Tracking Tools Today
Modern coffee consumers can now trace their favorite beans from farm to cup through sophisticated digital tracking tools that utilize blockchain technology and mobile applications.
You’ll find platforms like Farmer Connect and apps such as “Thank My Farmer” offering unprecedented supply chain visibility. Quality research-backed content provides consumers with reliable information about their coffee’s journey and origin claims.
These digital solutions enable you to:
- Scan QR codes to access detailed origin information
- View real-time tracking data throughout the supply chain
- Access brewing recommendations and tasting notes
- Verify sustainability certifications and fair trade practices
Through partnerships between tech firms and coffee companies, you’re now connected directly to farmers, ensuring transparency while supporting ethical practices and sustainable production methods.
Bean Processing Journey Stages
While coffee’s path from seed to cup spans multiple continents and processing stages, understanding each step reveals the meticulous care required to produce premium single-origin beans.
You’ll find your bean’s expedition begins with precise harvesting, where skilled farmers hand-pick only the ripest cherries.
Next, processors employ either dry or wet methods to transform these cherries, with fermentation developing distinct flavor profiles.
Through drying and milling, your beans undergo careful sorting and grading before they’re ready for roasting.
The final stage brings out your coffee’s unique characteristics through precise roasting and grinding, culminating in the brewing method you choose.
Water tanks play a crucial role during the fermentation process, allowing the beans to develop their signature flavors.
Ethical Sourcing and Sustainability
As sustainability standards become increasingly crucial in the coffee industry, ethical sourcing practices have evolved into fundamental requirements rather than optional features.
You’ll find that tracing your coffee’s path requires understanding key certification programs like C.A.F.E. Practices, Fairtrade, and Rainforest Alliance.
Major coffee companies like Starbucks source beans from over 400,000 farmers across multiple continents to maintain sustainable supply chains.
To verify your bean’s ethical sourcing:
- Check for certification labels indicating fair trade practices
- Research the origin’s farming methods and environmental practices
- Verify transparency in the supply chain documentation
- Examine direct trade relationships between roaster and farmer
These verification steps guarantee you’re supporting sustainable practices while contributing to the well-being of farming communities and environmental preservation.
The Technology Behind Coffee Traceability
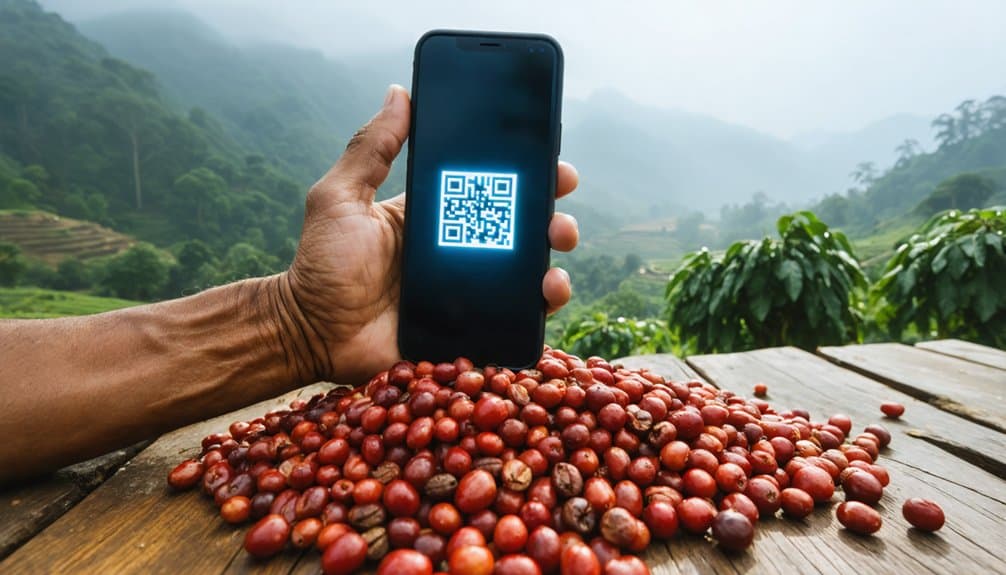

Building upon established ethical sourcing practices, sophisticated technologies now empower unprecedented transparency in coffee traceability.
You’ll find blockchain systems creating immutable records of your coffee’s expedition, while THz spectroscopy authenticates its geographical origins with 90% accuracy.
Isotopic analysis examines your beans’ unique fingerprints, revealing their precise growing conditions and altitude.
Through mobile applications integrated with blockchain, you can scan codes to access your coffee’s complete story – from farm coordinates to processing methods.
These interconnected technologies guarantee you’re getting exactly what you’ve paid for while supporting transparent, ethical trade.
The Wet Process method transforms coffee cherries through thorough washing that helps develop bright, clean flavors in the final cup.
FAQs
How Long Can I Store Single-Origin Coffee Beans Before They Lose Flavor?
You’ll get ideal flavor from single-origin beans within 2-3 weeks after roasting. If you’re storing them in airtight containers, you’ll maintain quality up to 6 months in cool, dark conditions.
Can Mixing Different Single-Origin Beans Create Better-Tasting Coffee Blends?
Like a symphony of flavors, you’ll find mixing single-origin beans can create superior blends, balancing each bean’s unique characteristics while achieving improved complexity, depth, and year-round consistency in your coffee experience.
Why Are Single-Origin Coffee Beans Typically More Expensive Than Regular Coffee?
You’ll find single-origin beans cost more because they’re cultivated in limited quantities, require meticulous farming practices, demand specific processing methods, and reflect higher certification and distribution expenses for their distinct characteristics.
Does Altitude Affect How I Should Brew My Single-Origin Coffee?
High-altitude beans grown above 4,000 feet need lighter roasts and pour-over brewing to highlight their complex acidity, while you’ll want darker roasts and cold brew methods for lower-altitude beans.
What’s the Best Way to Identify Counterfeit Single-Origin Coffee Products?
You’ll need to verify authenticity through HPLC-UV fingerprinting and physical examination. Check for origin-specific textures, colors, and certifications, while validating supplier documentation against established regulatory standards.
The Bottom Line
Through your meticulous analysis of digital traceability systems and geographic markers, you’ve mapped your coffee’s intricate expedition like a data scientist decoding DNA.
You’ve learned to dissect processing methods, scrutinize sustainability metrics, and validate authenticity protocols.
Armed with blockchain technology and precise origin data, you’re now equipped to trace your single-origin beans from their terroir to your cup with scientific precision.